
By The Economist
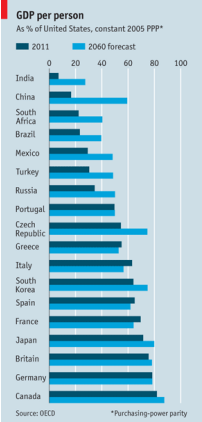
In rich, debt-laden economies the policymaking horizon is short-term: a recovery is the priority. Very long-range forecasts from the OECD, a think-tank, may seem an exercise in irrelevance. But they are a useful reminder of the economic and demographic factors that keep grinding away in the background.
In particular, the OECD’s projections for 2060 (at constant purchasing-power parities) show the impact of fast catch-up growth in underdeveloped countries with big populations. Economic power will tilt even more decisively away from the rich world than many realise. In 2011 the current membership of the OECD made up 65% of global output, compared with a combined 24% for China and India. By 2060 the two Asian giants will have a 46% share of world GDP, the OECD members a shrunken 42%. India’s economy will be a bit bigger than America’s, China’s a lot.
