By David DiSalvo
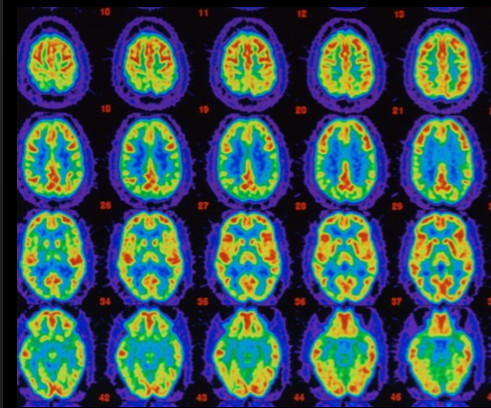
A new study from University of Virginia researchers supports a finding that’s been gaining science-fueled momentum in recent years: the human brain is wired to connect with others so strongly that it experiences what they experience as if it’s happening to us.
This would seem the neural basis for empathy—the ability to feel what others feel—but it goes even deeper than that. Results from the latest study suggest that our brains don’t differentiate between what happens to someone emotionally close to us and ourselves, and also that we seem neurally incapable of generating anything close to that level of empathy for strangers.
